Secrets Store CSI Driver and Reloader
Deploy Trivy Operator and Grafana Dashboard
Sometimes it is necessary to store secrets in services like HashiCorp Vault, AWS Secrets Manager, Azure Key Vault, or others, and then use them in Kubernetes.
In this post, I would like to explore how to store secrets in AWS Secrets Manager, retrieve them using the Kubernetes Secrets Store CSI Driver with the AWS Secrets and Configuration Provider (ASCP), and then use them both as Kubernetes Secrets and as files mounted directly into pods.
When a Secret is rotated and has been defined as an environment variable in the Pod specification (using secretKeyRef), it is necessary to refresh or restart the pod. This can be achieved using tools like Reloader.
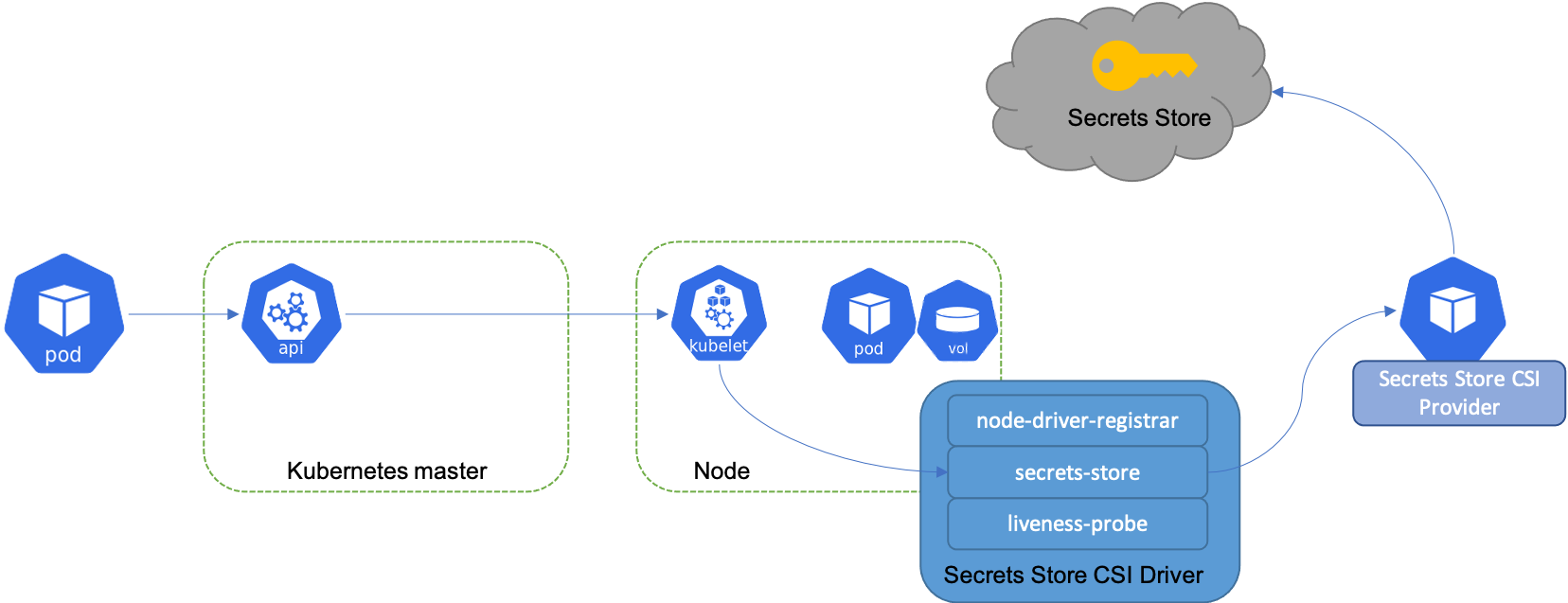 secrets-store-csi-driver architecture
secrets-store-csi-driver architecture
Links:
- Use AWS Secrets Manager secrets in Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service
- How to use AWS Secrets & Configuration Provider with your Kubernetes Secrets Store CSI driver
- Stakater Reloader docs
Requirements
- An Amazon EKS cluster (as described in “Cheapest Amazon EKS)”
- Helm
The following variables are used in the subsequent steps:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION="${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION:-us-east-1}"
export CLUSTER_FQDN="${CLUSTER_FQDN:-k01.k8s.mylabs.dev}"
export CLUSTER_NAME="${CLUSTER_FQDN%%.*}"
export TMP_DIR="${TMP_DIR:-${PWD}}"
export KUBECONFIG="${KUBECONFIG:-${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/kubeconfig-${CLUSTER_NAME}.conf}"
mkdir -pv "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}"
Create secret in AWS Secrets Manager
Use CloudFormation to create a Policy and Secrets in AWS Secrets Manager:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
cat > "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/aws-secretmanager-secret.yml" << \EOF
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: Secret Manager and policy
Parameters:
ClusterFQDN:
Description: "Cluster FQDN. (domain for all applications) Ex: kube1.k8s.mylabs.dev"
Type: String
Resources:
SecretsManagerKuardSecretPolicy:
Type: AWS::IAM::ManagedPolicy
Properties:
ManagedPolicyName: !Sub "${ClusterFQDN}-SecretsManagerKuardSecret"
Description: !Sub "Policy required by SecretsManager to access to Secrets Manager ${ClusterFQDN}-KuardSecret"
PolicyDocument:
Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Sid: SecretActions
Effect: Allow
Action:
- "secretsmanager:GetSecretValue"
- "secretsmanager:DescribeSecret"
Resource: !Ref SecretsManagerKuardSecret
SecretsManagerKuardSecret:
Type: AWS::SecretsManager::Secret
Properties:
Name: !Sub "${ClusterFQDN}-KuardSecret"
Description: My Secret
GenerateSecretString:
SecretStringTemplate: "{\"username\": \"admin123\"}"
GenerateStringKey: password
PasswordLength: 16
ExcludePunctuation: true
Outputs:
SecretsManagerKuardSecretArn:
Description: The ARN of the created Amazon SecretsManagerKuardSecret Secret
Value: !Ref SecretsManagerKuardSecret
SecretsManagerKuardSecretPolicyArn:
Description: The ARN of the created SecretsManagerKuardSecret Policy
Value: !Ref SecretsManagerKuardSecretPolicy
EOF
aws cloudformation deploy --capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM \
--parameter-overrides "ClusterFQDN=${CLUSTER_FQDN}" \
--stack-name "${CLUSTER_NAME}-aws-secretmanager-secret" --template-file "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/aws-secretmanager-secret.yml"
Screenshot from AWS Secrets Manager:
 AWS Secrets Manager - Secrets - k01.k8s.mylabs.dev-KuardSecret
AWS Secrets Manager - Secrets - k01.k8s.mylabs.dev-KuardSecret
Install Secrets Store CSI Driver and AWS Provider
Install the secrets-store-csi-driver Helm chart and modify its default values:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# renovate: datasource=helm depName=secrets-store-csi-driver registryUrl=https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/secrets-store-csi-driver/charts
SECRETS_STORE_CSI_DRIVER_HELM_CHART_VERSION="1.4.1"
helm repo add --force-update secrets-store-csi-driver https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/secrets-store-csi-driver/charts
cat > "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-secrets-store-csi-driver.yml" << EOF
syncSecret:
enabled: true
enableSecretRotation: true
EOF
helm upgrade --install --version "${SECRETS_STORE_CSI_DRIVER_HELM_CHART_VERSION}" --namespace secrets-store-csi-driver --create-namespace --wait --values "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-secrets-store-csi-driver.yml" secrets-store-csi-driver secrets-store-csi-driver/secrets-store-csi-driver
Install the secrets-store-csi-driver-provider-aws Helm chart:
1
2
3
4
5
# renovate: datasource=helm depName=secrets-store-csi-driver-provider-aws registryUrl=https://aws.github.io/secrets-store-csi-driver-provider-aws
SECRETS_STORE_CSI_DRIVER_PROVIDER_AWS_HELM_CHART_VERSION="0.3.6"
helm repo add --force-update aws-secrets-manager https://aws.github.io/secrets-store-csi-driver-provider-aws
helm upgrade --install --version "${SECRETS_STORE_CSI_DRIVER_PROVIDER_AWS_HELM_CHART_VERSION}" --namespace secrets-store-csi-driver --create-namespace --wait secrets-store-csi-driver-provider-aws aws-secrets-manager/secrets-store-csi-driver-provider-aws
The necessary components are now ready.
Install kuard
Kuard is a simple application that can be used to display various pod details, created for the book “Kubernetes: Up and Running”.
Install Kuard, which will use the secrets from AWS Secrets Manager as a mountpoint and also as a Kubernetes Secret.
1
2
SECRETS_MANAGER_KUARDSECRET_POLICY_ARN=$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name "${CLUSTER_NAME}-aws-secretmanager-secret" --query "Stacks[0].Outputs[?OutputKey==\`SecretsManagerKuardSecretPolicyArn\`].OutputValue" --output text)
eksctl create iamserviceaccount --cluster="${CLUSTER_NAME}" --name=kuard --namespace=kuard --attach-policy-arn="${SECRETS_MANAGER_KUARDSECRET_POLICY_ARN}" --role-name="eksctl-${CLUSTER_NAME}-irsa-kuard" --approve
Create the SecretProviderClass. This object tells the AWS provider which secrets to mount in the pod. It will also create a Secret named kuard-secret that will be synchronized with the data stored in AWS Secrets Manager.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
kubectl apply -f - << EOF
apiVersion: secrets-store.csi.x-k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: SecretProviderClass
metadata:
name: kuard-deployment-aws-secrets
namespace: kuard
spec:
provider: aws
parameters:
objects: |
- objectName: "${CLUSTER_FQDN}-KuardSecret"
objectType: "secretsmanager"
objectAlias: KuardSecret
secretObjects:
- secretName: kuard-secret
type: Opaque
data:
- objectName: KuardSecret
key: username
EOF
Install Kuard and use the previously created SecretProviderClass:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
kubectl apply -f - << EOF
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: kuard
namespace: kuard
labels:
app: kuard
spec:
selector:
app: kuard
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 8080
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: kuard-deployment
namespace: kuard
labels:
app: kuard
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: kuard
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: kuard
spec:
serviceAccountName: kuard
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- topologyKey: "kubernetes.io/hostname"
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
app: kuard
volumes:
- name: secrets-store-inline
csi:
driver: secrets-store.csi.k8s.io
readOnly: true
volumeAttributes:
secretProviderClass: "kuard-deployment-aws-secrets"
containers:
- name: kuard-deployment
# renovate: datasource=docker depName=gcr.io/kuar-demo/kuard-arm64 extractVersion=^(?<version>.+)$
image: gcr.io/kuar-demo/kuard-arm64:v0.9-green
resources:
requests:
cpu: 10m
memory: "32Mi"
limits:
cpu: 20m
memory: "64Mi"
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
volumeMounts:
- name: secrets-store-inline
mountPath: "/mnt/secrets-store"
readOnly: true
env:
- name: KUARDSECRET
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: kuard-secret
key: username
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: kuard
namespace: kuard
annotations:
forecastle.stakater.com/expose: "true"
forecastle.stakater.com/icon: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/d9a58a39b69a0eaec5797e0f7a0f9472b4829ab0/logo/logo_with_border.svg
forecastle.stakater.com/appName: Kuard
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-url: https://oauth2-proxy.${CLUSTER_FQDN}/oauth2/auth
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-signin: https://oauth2-proxy.${CLUSTER_FQDN}/oauth2/start?rd=\$scheme://\$host\$request_uri
labels:
app: kuard
spec:
rules:
- host: kuard.${CLUSTER_FQDN}
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
backend:
service:
name: kuard
port:
number: 8080
tls:
- hosts:
- kuard.${CLUSTER_FQDN}
EOF
After the successful deployment of Kuard, you should see the credentials in the kuard-secret:
1
2
kubectl wait --namespace kuard --for condition=available deployment kuard-deployment
kubectl get secrets -n kuard kuard-secret --template="{{.data.username}}" | base64 -d | jq
1
2
3
4
{
"password": "rxxxxxxxxxxxxxxH",
"username": "admin123"
}
You should see similar log messages in the secrets-store-csi-driver pods:
1
kubectl logs -n secrets-store-csi-driver daemonsets/secrets-store-csi-driver
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Found 2 pods, using pod/secrets-store-csi-driver-2k9jv
I0416 12:17:32.553991 1 exporter.go:35] "initializing metrics backend" backend="prometheus"
I0416 12:17:32.555766 1 main.go:190] "starting manager\n"
I0416 12:17:32.656785 1 secrets-store.go:46] "Initializing Secrets Store CSI Driver" driver="secrets-store.csi.k8s.io" version="v1.3.2" buildTime="2023-03-20-21:09"
I0416 12:17:32.656834 1 reconciler.go:130] "starting rotation reconciler" rotationPollInterval="2m0s"
I0416 12:17:32.660649 1 server.go:121] "Listening for connections" address="//csi/csi.sock"
I0416 12:17:34.082277 1 nodeserver.go:365] "node: getting default node info\n"
I0416 12:18:54.990977 1 nodeserver.go:359] "Using gRPC client" provider="aws" pod="kuard-deployment-756f6cd885-6mzrq"
I0416 12:18:56.015817 1 nodeserver.go:254] "node publish volume complete" targetPath="/var/lib/kubelet/pods/ba66d6a4-1def-4636-b67a-99ca929e9293/volumes/kubernetes.io~csi/secrets-store-inline/mount" pod="kuard/kuard-deployment-756f6cd885-6mzrq" time="1.128414837s"
I0416 12:18:56.016290 1 secretproviderclasspodstatus_controller.go:222] "reconcile started" spcps="kuard/kuard-deployment-756f6cd885-6mzrq-kuard-kuard-deployment-aws-secrets"
I0416 12:18:56.220255 1 secretproviderclasspodstatus_controller.go:366] "reconcile complete" spc="kuard/kuard-deployment-aws-secrets" pod="kuard/kuard-deployment-756f6cd885-6mzrq" spcps="kuard/kuard-deployment-756f6cd885-6mzrq-kuard-kuard-deployment-aws-secrets"
Go to these URLs and check the credentials synced from AWS Secrets Manager:
https://kuard.k01.k8s.mylabs.dev/fs/mnt/secrets-store/

1
kubectl exec -i -n kuard deployments/kuard-deployment -- cat /mnt/secrets-store/KuardSecret
1
{"password":"rxxxxxxxxxxxxxxH","username":"admin123"}
https://kuard.k01.k8s.mylabs.dev/-/env

1
kubectl exec -i -n kuard deployments/kuard-deployment -- sh -c "echo \${KUARDSECRET}"
1
{"password":"rxxxxxxxxxxxxxxH","username":"admin123"}
After executing the commands above, the secret from AWS Secrets Manager is copied to the Kubernetes Secret (kuard-secret). It is also present as a file (/mnt/secrets-store/KuardSecret) and as an environment variable (KUARDSECRET) inside the pod.
Rotate AWS Secret
Let’s change/rotate the credentials inside the AWS Secret to see if the change will also be reflected in the Kubernetes objects:
1
2
3
aws secretsmanager update-secret --secret-id "k01.k8s.mylabs.dev-KuardSecret" \
--secret-string "{\"user\":\"admin123\",\"password\":\"EXAMPLE-PASSWORD\"}"
sleep 200
After changing the password in AWS Secrets Manager, you should also see the change in the Kubernetes Secret and in the /mnt/secrets-store/KuardSecret file inside the pod:
1
kubectl get secrets -n kuard kuard-secret --template="{{.data.username}}" | base64 -d | jq
1
2
3
4
{
"user": "admin123",
"password": "EXAMPLE-PASSWORD"
}
 AWS Secrets Manager - Secrets - k01.k8s.mylabs.dev-KuardSecret
AWS Secrets Manager - Secrets - k01.k8s.mylabs.dev-KuardSecret
1
kubectl exec -i -n kuard deployments/kuard-deployment -- cat /mnt/secrets-store/KuardSecret
1
{"user":"admin123","password":"EXAMPLE-PASSWORD"}
The environment variable inside the pod will not be changed automatically:
1
kubectl exec -i -n kuard deployments/kuard-deployment -- sh -c "echo \${KUARDSECRET}"
1
{"password":"rxxxxxxxxxxxxxxH","username":"admin123"}
The only way to update a pre-defined environment variable inside the pod is to restart the pod.
Install Reloader to do rolling upgrades when Secrets get changed
In the case of changes to the Secret (kuard-secret), a rolling upgrade should be performed on the Deployment (kuard-deployment) to “refresh” the environment variables.
It is time to use Reloader, which can perform this action automatically.
Install the reloader Helm chart:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# renovate: datasource=helm depName=reloader registryUrl=https://stakater.github.io/stakater-charts
RELOADER_HELM_CHART_VERSION="1.0.69"
helm repo add --force-update stakater https://stakater.github.io/stakater-charts
cat > "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-reloader.yml" << EOF
reloader:
readOnlyRootFileSystem: true
podMonitor:
enabled: true
EOF
helm upgrade --install --version "${RELOADER_HELM_CHART_VERSION}" --namespace reloader --create-namespace --wait --values "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-reloader.yml" reloader stakater/reloader
You need to annotate the kuard deployment to enable Pod rolling upgrades:
1
kubectl annotate -n kuard deployment kuard-deployment 'reloader.stakater.com/auto=true'
Let’s perform the credential change one more time:
1
2
3
aws secretsmanager update-secret --secret-id "k01.k8s.mylabs.dev-KuardSecret" \
--secret-string "{\"user\":\"admin123\",\"password\":\"EXAMPLE-PASSWORD-2\"}"
sleep 400
Screenshot from AWS Secrets Manager:
 AWS Secrets Manager - Secrets - k01.k8s.mylabs.dev-KuardSecret
AWS Secrets Manager - Secrets - k01.k8s.mylabs.dev-KuardSecret
After some time, changes are detected in the kuard-secret secret, and the pods are restarted:
1
kubectl logs -n reloader deployments/reloader-reloader reloader-reloader
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
time="2023-04-17T18:08:57Z" level=info msg="Environment: Kubernetes"
time="2023-04-17T18:08:57Z" level=info msg="Starting Reloader"
time="2023-04-17T18:08:57Z" level=warning msg="KUBERNETES_NAMESPACE is unset, will detect changes in all namespaces."
time="2023-04-17T18:08:57Z" level=info msg="created controller for: configMaps"
time="2023-04-17T18:08:57Z" level=info msg="Starting Controller to watch resource type: configMaps"
time="2023-04-17T18:08:57Z" level=info msg="created controller for: secrets"
time="2023-04-17T18:08:57Z" level=info msg="Starting Controller to watch resource type: secrets"
time="2023-04-17T18:12:17Z" level=info msg="Changes detected in 'kuard-secret' of type 'SECRET' in namespace 'kuard', Updated 'kuard-deployment' of type 'Deployment' in namespace 'kuard'"
After the pods reload, the environment variable KUARDSECRET should contain the updated value:
1
kubectl exec -i -n kuard deployments/kuard-deployment -- sh -c "echo \${KUARDSECRET}"
1
{"user":"admin123","password":"EXAMPLE-PASSWORD-2"}
It is possible to use and synchronize credentials from AWS Secrets Manager to the following locations within a pod:
- A file inside the pod
- A Kubernetes Secret
- An environment variable inside the pod
To clean up the environment, delete the IRSA, remove the CloudFormation stack, and delete the namespace:
1
2
3
4
if eksctl get iamserviceaccount --cluster="${CLUSTER_NAME}" --name=kuard --namespace=kuard; then
eksctl delete iamserviceaccount --cluster="${CLUSTER_NAME}" --name=kuard --namespace=kuard
fi
aws cloudformation delete-stack --stack-name "${CLUSTER_NAME}-aws-secretmanager-secret"
Remove files from the ${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN} directory:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
for FILE in "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}"/{aws-secretmanager-secret,helm_values-{reloader,secrets-store-csi-driver}}.yml; do
if [[ -f "${FILE}" ]]; then
rm -v "${FILE}"
else
echo "*** File not found: ${FILE}"
fi
done
Enjoy … 😉
